Hello Readers,
In the last blog post, we saw about BIOS and its role. I want to share more about UEFI. UEFI stands for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware.
Basic Difference in technology
BIOS used to use Master Boot Record (MBR) for some of its services. I will not go in depth of MBR as it is out of the scope of this blog post, but for now, consider that MBR is used by BIOS for doing specific tasks. MBR was getting obsolete due to its limitation in handling large partitions(Partition means your drives like C, D E etc) in the hard disk. Due to MBR, hard drives and SSDs were able to handle partitions only up to 2 TeraBytes(TB). In early days 2TB was used to consider a very large space, but nowadays having hard disk or SSD in TBs is not a big deal! UEFI can handle up to Petabytes(PB) partitions and even high graphics card. UEFI uses a GUID partition table instead of MBR. UEFI is also faster and have greater
One more significant advantage of UEFI is that it provides the feature called secured boot. Secure boot feature can protect you from malicious software and hacking.
Difference in user-interface

( Hit F2 on
BIOS menu used to have very smile graphics and interface. Usually no one other than computer technician was able to understand it. But the UEFI provides a user-friendly interface and anyone can easily understand and use it.
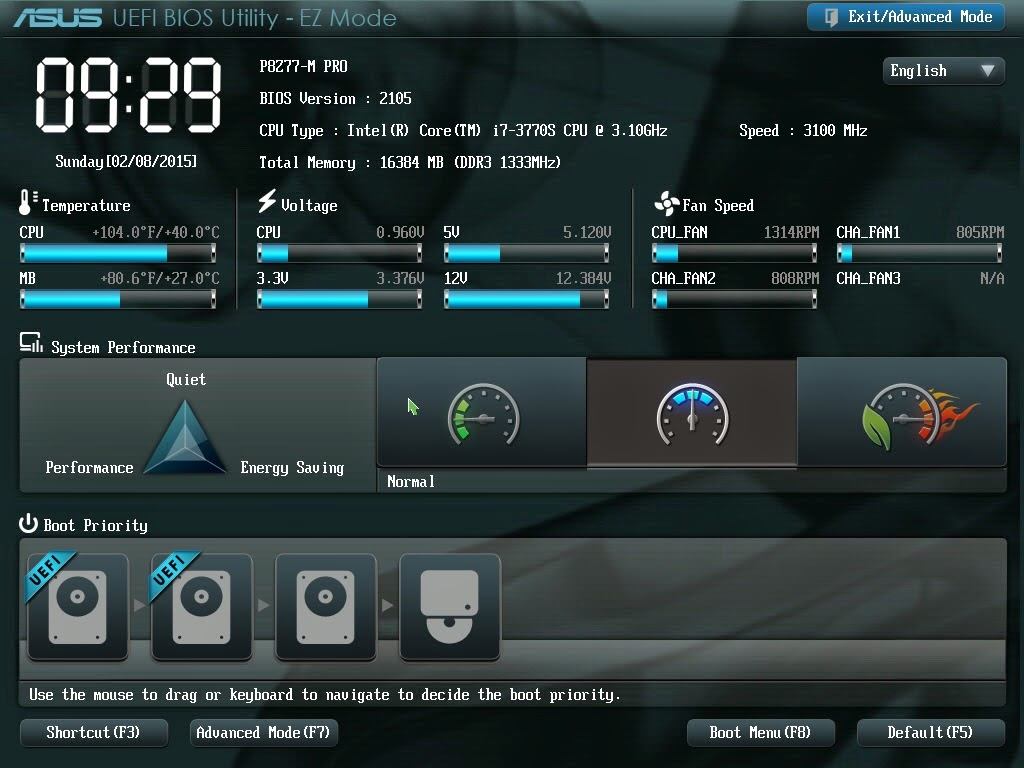
(Image Source: https://www.4winkey.com/images/article/computer-help/asus-uefi-usb.jpg )
Take Away
- UEFI is
successor of BIOS. - UEFI performs all tasks as performed by BIOS along with some additional tasks like
secure boot. - UEFI can handle more storage size HDDs and SSDs.
- UEFI has better user-interface than BIOS.